LeetCode21. 合并两个有序链表🌟🌟🌟简单
问题描述
原文链接:21. 合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
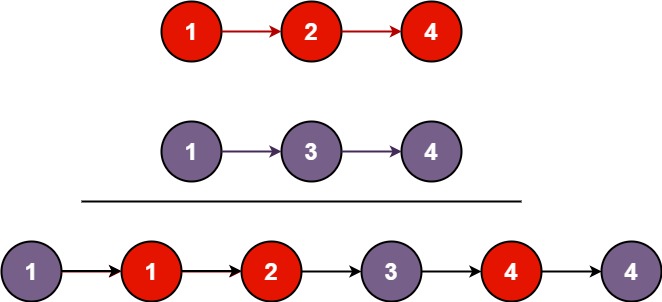
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是
[0, 50] -100 <= Node.val <= 100l1和l2均按 非递减顺序 排列
代码实现
Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// 视频里忘了说,其实这个判断可以优化掉,下面的逻辑已经包含了
// if(list1 == null){
// return list2;
// }
// if(list2 == null){
// return list1;
// }
ListNode list3 = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode temp = list3;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val <= list2.val){
temp.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
temp.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
// if(list1 != null){
// temp.next = list1;
// }
// if(list2 != null){
// temp.next = list2;
// }
// 上面两个也能优化一下,我视频里也忘了说
temp.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1;
return list3.next;
}
}
Python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1, list2):
"""
:type list1: Optional[ListNode]
:type list2: Optional[ListNode]
:rtype: Optional[ListNode]
"""
# 视频里忘了说,其实这个判断可以优化掉,下面的逻辑已经包含了
# if(list1 == null){
# return list2;
# }
# if(list2 == null){
# return list1;
# }
list3 = ListNode(-1)
temp = list3
while list1 != None and list2 != None:
if list1.val <= list2.val:
temp.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
else:
temp.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
temp = temp.next
# if list1 != None:
# temp.next = list1
# if list2 != None:
# temp.next = list2
# 上面两个也能优化一下,我视频里也忘了说
temp.next = list1 if list1 != None else list2
return list3.next
C++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
// 视频里忘了说,其实这个判断可以优化掉,下面的逻辑已经包含了
// if(list1 == null){
// return list2;
// }
// if(list2 == null){
// return list1;
// }
ListNode* list3 = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* temp = list3;
while(list1 != nullptr && list2 != nullptr){
if(list1->val <= list2->val){
temp->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
} else {
temp->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
// if(list1 != nullptr){
// temp->next = list1;
// }
// if(list2 != nullptr){
// temp->next = list2;
// }
// 上面两个也能优化一下,我视频里也忘了说
temp->next = list1 == nullptr ? list2 : list1;
return list3->next;
}
};
Go
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func mergeTwoLists(list1 *ListNode, list2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
// 视频里忘了说,其实这个判断可以优化掉,下面的逻辑已经包含了
// if(list1 == nil){
// return list2;
// }
// if(list2 == nil){
// return list1;
// }
list3 := &ListNode{Val: -1}
temp := list3
for list1 != nil && list2 != nil {
if list1.Val <= list2.Val {
temp.Next = list1
list1 = list1.Next
} else {
temp.Next = list2
list2 = list2.Next
}
temp = temp.Next
}
// if list1 != nil {
// temp.Next = list1
// }
// if list2 != nil {
// temp.Next = list2
// }
// 上面两个也能优化一下,我视频里也忘了说
if list1 == nil {
temp.Next = list2
} else {
temp.Next = list1
}
return list3.Next
}
