二叉树最大宽度 🌟🌟🌟中等
课后作业
问题描述
原文链接:662. 二叉树最大宽度
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回树的最大宽度。
树的最大宽度是所有层中最大的宽度。
每一层的宽度被定义为该层最左和最右的非空节点(即,两个端点)之间的长度。将这个二叉树视作与满二叉树结构相同,两端点间会出现一些延伸到这一层的 null 节点,这些 null 节点也计入长度。
题目数据保证答案将会在32位 带符号整数范围内。
示例 1:
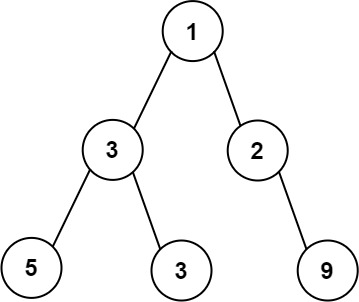
输入:root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
输出:4
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 3 层,宽度为 4 (5,3,null,9) 。
示例 2:
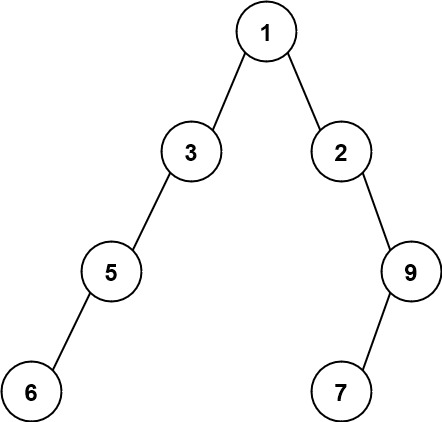
输入:root = [1,3,2,5,null,null,9,6,null,7]
输出:7
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 4 层,宽度为 7 (6,null,null,null,null,null,7) 。
示例 3:
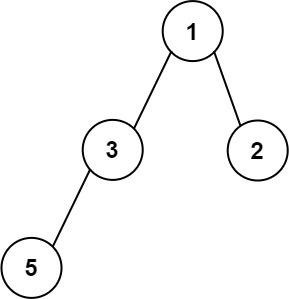
输入:root = [1,3,2,5]
输出:2
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 2 层,宽度为 2 (3,2) 。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[1, 3000] -100 <= Node.val <= 100
代码实现
Java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
Queue<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int max = 0;
queue.add(new Pair<TreeNode, Integer>(root, 1));
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
List<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
Pair<TreeNode, Integer> temp = queue.poll();
// key-value
TreeNode key = temp.getKey();
int value = temp.getValue();
res.add(temp);
if(key.left != null){
queue.add(new Pair<TreeNode, Integer>(key.left, value * 2));
}
if(key.right != null){
queue.add(new Pair<TreeNode, Integer>(key.right, value * 2 + 1));
}
}
int t = res.get(res.size() - 1).getValue() - res.get(0).getValue() + 1;
max = Math.max(max, t);
}
return max;
}
}
Python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def widthOfBinaryTree(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
if not root:
return 0
queue = [(root, 1)]
maximum = 0
while queue:
size = len(queue)
res = []
for i in range(size):
temp = queue.pop(0)
res.append(temp)
if temp[0].left:
queue.append((temp[0].left, temp[1] * 2))
if temp[0].right:
queue.append((temp[0].right, temp[1] * 2 + 1))
t = res[-1][1] - res[0][1] + 1
maximum = max(maximum, t)
return maximum
C++
class Solution {
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
queue<pair<TreeNode*, unsigned long long>> q;
int max_width = 0;
q.push(make_pair(root, 1));
while (!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
vector<pair<TreeNode*, unsigned long long>> level_nodes;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
auto node = q.front().first;
auto pos = q.front().second;
q.pop();
level_nodes.push_back(make_pair(node, pos));
if (node->left) {
q.push(make_pair(node->left, pos * 2));
}
if (node->right) {
q.push(make_pair(node->right, pos * 2 + 1));
}
}
unsigned long long level_width = level_nodes.back().second - level_nodes.front().second + 1;
max_width = max(max_width, (int)level_width);
}
return max_width;
}
};
Go
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func widthOfBinaryTree(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
queue := []*Pair{{root, 1}}
var max int
for len(queue) > 0 {
size := len(queue)
res := []*Pair{}
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
temp := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
res = append(res, temp)
if temp.Key.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, &Pair{temp.Key.Left, temp.Value * 2})
}
if temp.Key.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, &Pair{temp.Key.Right, temp.Value * 2 + 1})
}
}
t := res[len(res)-1].Value - res[0].Value + 1
max = int(math.Max(float64(max), float64(t)))
}
return max
}
type Pair struct {
Key *TreeNode
Value int
}
